What are the Side effects of Botulinum toxin injection? - Explained by Dr. Yeung Ho Hong (楊浩康)
Dr Yeung Ho Hong ( 楊浩康 醫生 )
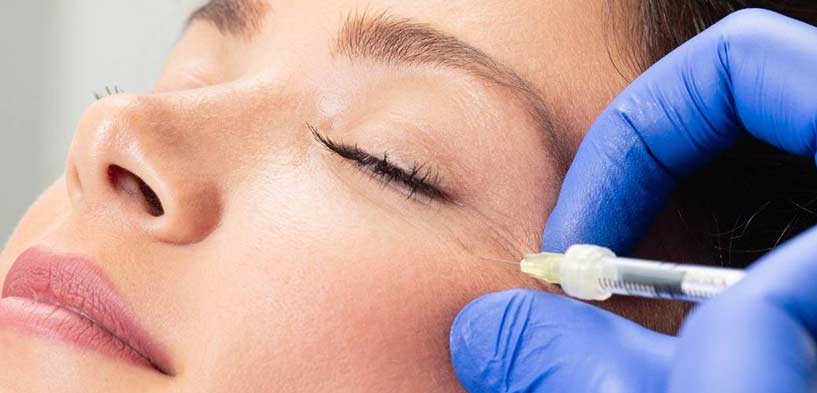
Botulinum toxin (肉毒桿菌毒素) is widely used in medical aesthetics, primarily to reduce facial dynamic wrinkles and contour the face. However, as highlighted by various media reports and research studies, this technique is not 100% safe. Some individuals who have undergone injections have experienced a range of side effects, prompting many to seek a thorough understanding of the associated risks before choosing treatment. This article will explore in detail the mechanism of action of botulinum toxin, its potential side effects, and key considerations, aiming to provide comprehensive reference information.
First, it’s essential to understand how botulinum toxin works clinically. When injected into targeted muscles, the toxin blocks the release of acetylcholine at nerve endings, preventing normal muscle contraction. This temporary nerve blockade effectively reduces dynamic wrinkles caused by repeated muscle movement, resulting in smoother, tighter skin. However, if not performed carefully, this process can lead to impaired muscle function or unintended changes.
Common risks of botulinum toxin injections include overcorrection and undercorrection. Overcorrection occurs when the targeted muscle becomes overly relaxed post-injection, producing a “puppet-like face” effect, where facial expressions appear stiff or unnatural. Undercorrection, conversely, may fail to achieve the desired aesthetic outcome, leaving wrinkles still visible. Additionally, because injection sites interact with nearby muscle anatomy, facial asymmetry can sometimes occur post-injection, disrupting the natural balance of the face.
More seriously, if botulinum toxin spreads to adjacent muscles during injection, it can trigger additional adverse reactions. For example, if the toxin inadvertently spreads to the muscles controlling the eyelids, it may cause eyelid drooping (ptosis). Similarly, if it affects the muscles around the mouth or cheeks, it could lead to asymmetrical or drooping mouth corners, impacting speech and eating functions. Although these side effects are typically temporary and improve as the toxin is metabolized, they can still inconvenience the patient’s appearance and daily life during the treatment period.
Moreover, repeated botulinum toxin injections over time may increase the risk of muscle atrophy. Prolonged muscle relaxation can gradually diminish the muscle’s natural vitality and tone, potentially leading to permanent atrophy and loss of function in the affected area. While this condition is rare, it underscores the need for patients to carefully evaluate their needs and follow professional medical advice when considering this treatment.
The effectiveness and duration of botulinum toxin typically depend on the treatment site, individual metabolism, and lifestyle factors. Generally, the improvement lasts about 4 to 6 months post-injection, though responses vary among patients. Some may notice a significant rebound as the effects begin to fade, while others may maintain good results for a longer period. Thus, thorough pre-treatment communication with a physician to develop a personalized plan is vital—not only to optimize outcomes but also to minimize unnecessary side effects.
In addition to the risks mentioned, short-term reactions such as localized redness, bruising, mild pain, or a burning sensation may occur, which are usually normal inflammatory responses post-treatment and resolve within a few days in most cases. Due to individual differences, some patients may also experience headaches, neck discomfort, or temporary nerve dysfunction. While these adverse effects are generally transient, they still require close monitoring by a physician to ensure prompt management and relief.
When opting for botulinum toxin treatment, patients should prioritize experienced, skilled professionals. Proper injection techniques, precise dosage control, and a deep understanding of facial anatomy are critical to reducing the risk of side effects. Additionally, detailed pre-treatment consultation and health assessments are essential, including inquiries about the patient’s allergy history, neuromuscular disease history, and recent use of other medications. This information helps physicians devise safer treatment plans.
It’s worth noting that certain groups, such as pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, or patients with neurological disorders, require extra caution with botulinum toxin treatment. These individuals may be more sensitive to the drug’s components, increasing the risk of adverse reactions post-treatment. Physicians typically recommend postponing such treatments to avoid potential long-term health impacts.
In summary, botulinum toxin as a treatment for improving facial dynamic wrinkles, offers reliable safety and efficacy when administered by experienced professionals, yet its potential risks and side effects cannot be overlooked. From over- or undercorrection to localized muscle dysfunction and possible long-term muscle atrophy, each issue serves as a reminder that, while pursuing beauty, patients must remain highly vigilant about treatment safety. Only by fully understanding these risks, selecting a reputable medical facility, and following physician guidance can patients enjoy the cosmetic benefits while minimizing the likelihood of adverse reactions.
